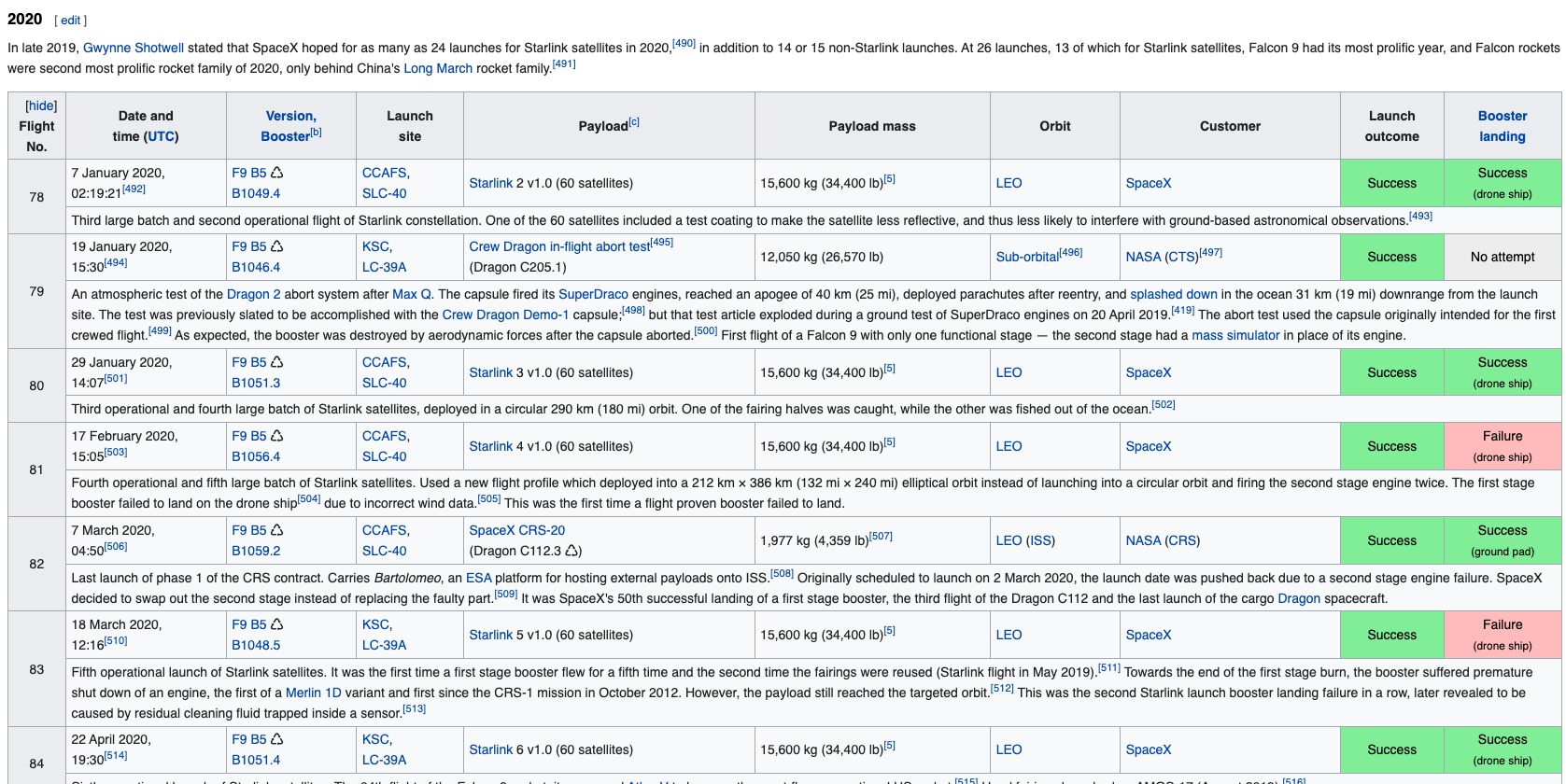
<table class="wikitable plainrowheaders collapsible" style="width: 100%;">
<tbody><tr>
<th scope="col">Flight No.
</th>
<th scope="col">Date and<br/>time (<a href="/wiki/Coordinated_Universal_Time" title="Coordinated Universal Time">UTC</a>)
</th>
<th scope="col"><a href="/wiki/List_of_Falcon_9_first-stage_boosters" title="List of Falcon 9 first-stage boosters">Version,<br/>Booster</a> <sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-booster_11-0"><a href="#cite_note-booster-11">[b]</a></sup>
</th>
<th scope="col">Launch site
</th>
<th scope="col">Payload<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-Dragon_12-0"><a href="#cite_note-Dragon-12">[c]</a></sup>
</th>
<th scope="col">Payload mass
</th>
<th scope="col">Orbit
</th>
<th scope="col">Customer
</th>
<th scope="col">Launch<br/>outcome
</th>
<th scope="col"><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_first-stage_landing_tests" title="Falcon 9 first-stage landing tests">Booster<br/>landing</a>
</th></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">1
</th>
<td>4 June 2010,<br/>18:45
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.0" title="Falcon 9 v1.0">F9 v1.0</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-0"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B0003.1<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-0"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Dragon_Spacecraft_Qualification_Unit" title="Dragon Spacecraft Qualification Unit">Dragon Spacecraft Qualification Unit</a>
</td>
<td>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SpaceX" title="SpaceX">SpaceX</a>
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success
</td>
<td class="table-failure" style="background: #FFC7C7; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Failure<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-ns20110930_15-0"><a href="#cite_note-ns20110930-15">[9]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-16"><a href="#cite_note-16">[10]</a></sup><br/><small>(parachute)</small>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">First flight of Falcon 9 v1.0.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sfn20100604_17-0"><a href="#cite_note-sfn20100604-17">[11]</a></sup> Used a boilerplate version of Dragon capsule which was not designed to separate from the second stage.<small>(<a href="#First_flight_of_Falcon_9">more details below</a>)</small> Attempted to recover the first stage by parachuting it into the ocean, but it burned up on reentry, before the parachutes even deployed.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-parachute_18-0"><a href="#cite_note-parachute-18">[12]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">2
</th>
<td>8 December 2010,<br/>15:43<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-spaceflightnow_Clark_Launch_Report_19-0"><a href="#cite_note-spaceflightnow_Clark_Launch_Report-19">[13]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.0" title="Falcon 9 v1.0">F9 v1.0</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-1"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B0004.1<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-1"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SpaceX_Dragon" title="SpaceX Dragon">Dragon</a> <a class="mw-redirect" href="/wiki/COTS_Demo_Flight_1" title="COTS Demo Flight 1">demo flight C1</a><br/>(Dragon C101)
</td>
<td>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a> (<a href="/wiki/International_Space_Station" title="International Space Station">ISS</a>)
</td>
<td><div class="plainlist">
<ul><li><a href="/wiki/NASA" title="NASA">NASA</a> (<a href="/wiki/Commercial_Orbital_Transportation_Services" title="Commercial Orbital Transportation Services">COTS</a>)</li>
<li><a href="/wiki/National_Reconnaissance_Office" title="National Reconnaissance Office">NRO</a></li></ul>
</div>
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-ns20110930_15-1"><a href="#cite_note-ns20110930-15">[9]</a></sup>
</td>
<td class="table-failure" style="background: #FFC7C7; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Failure<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-ns20110930_15-2"><a href="#cite_note-ns20110930-15">[9]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-20"><a href="#cite_note-20">[14]</a></sup><br/><small>(parachute)</small>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">Maiden flight of <a class="mw-redirect" href="/wiki/Dragon_capsule" title="Dragon capsule">Dragon capsule</a>, consisting of over 3 hours of testing thruster maneuvering and reentry.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-spaceflightnow_Clark_unleashing_Dragon_21-0"><a href="#cite_note-spaceflightnow_Clark_unleashing_Dragon-21">[15]</a></sup> Attempted to recover the first stage by parachuting it into the ocean, but it disintegrated upon reentry, before the parachutes were deployed.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-parachute_18-1"><a href="#cite_note-parachute-18">[12]</a></sup> <small>(<a href="#COTS_demo_missions">more details below</a>)</small> It also included two <a href="/wiki/CubeSat" title="CubeSat">CubeSats</a>,<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-NRO_Taps_Boeing_for_Next_Batch_of_CubeSats_22-0"><a href="#cite_note-NRO_Taps_Boeing_for_Next_Batch_of_CubeSats-22">[16]</a></sup> and a wheel of <a href="/wiki/Brou%C3%A8re" title="Brouère">Brouère</a> cheese.
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">3
</th>
<td>22 May 2012,<br/>07:44<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-BBC_new_era_23-0"><a href="#cite_note-BBC_new_era-23">[17]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.0" title="Falcon 9 v1.0">F9 v1.0</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-2"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B0005.1<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-2"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SpaceX_Dragon" title="SpaceX Dragon">Dragon</a> <a class="mw-redirect" href="/wiki/Dragon_C2%2B" title="Dragon C2+">demo flight C2+</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-C2_24-0"><a href="#cite_note-C2-24">[18]</a></sup><br/>(Dragon C102)
</td>
<td>525 kg (1,157 lb)<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-25"><a href="#cite_note-25">[19]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a> (<a href="/wiki/International_Space_Station" title="International Space Station">ISS</a>)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/NASA" title="NASA">NASA</a> (<a href="/wiki/Commercial_Orbital_Transportation_Services" title="Commercial Orbital Transportation Services">COTS</a>)
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-26"><a href="#cite_note-26">[20]</a></sup>
</td>
<td class="table-noAttempt" style="background: #EEE; vertical-align: middle; white-space: nowrap; text-align: center;">No attempt
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">Dragon spacecraft demonstrated a series of tests before it was allowed to approach the <a href="/wiki/International_Space_Station" title="International Space Station">International Space Station</a>. Two days later, it became the first commercial spacecraft to board the ISS.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-BBC_new_era_23-1"><a href="#cite_note-BBC_new_era-23">[17]</a></sup> <small>(<a href="#COTS_demo_missions">more details below</a>)</small>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="3" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">4
</th>
<td rowspan="2">8 October 2012,<br/>00:35<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-SFN_LLog_27-0"><a href="#cite_note-SFN_LLog-27">[21]</a></sup>
</td>
<td rowspan="2"><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.0" title="Falcon 9 v1.0">F9 v1.0</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-3"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B0006.1<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-3"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td rowspan="2"><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SpaceX_CRS-1" title="SpaceX CRS-1">SpaceX CRS-1</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxManifest20120925_28-0"><a href="#cite_note-sxManifest20120925-28">[22]</a></sup><br/>(Dragon C103)
</td>
<td>4,700 kg (10,400 lb)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a> (<a href="/wiki/International_Space_Station" title="International Space Station">ISS</a>)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/NASA" title="NASA">NASA</a> (<a href="/wiki/Commercial_Resupply_Services" title="Commercial Resupply Services">CRS</a>)
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success
</td>
<td rowspan="2" style="background:#ececec; text-align:center;"><span class="nowrap">No attempt</span>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="/wiki/Orbcomm_(satellite)" title="Orbcomm (satellite)">Orbcomm-OG2</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-Orbcomm_29-0"><a href="#cite_note-Orbcomm-29">[23]</a></sup>
</td>
<td>172 kg (379 lb)<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-gunter-og2_30-0"><a href="#cite_note-gunter-og2-30">[24]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Orbcomm" title="Orbcomm">Orbcomm</a>
</td>
<td class="table-partial" style="background: #FE9; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Partial failure<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-nyt-20121030_31-0"><a href="#cite_note-nyt-20121030-31">[25]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">CRS-1 was successful, but the <a href="/wiki/Secondary_payload" title="Secondary payload">secondary payload</a> was inserted into an abnormally low orbit and subsequently lost. This was due to one of the nine <a href="/wiki/SpaceX_Merlin" title="SpaceX Merlin">Merlin engines</a> shutting down during the launch, and NASA declining a second reignition, as per <a href="/wiki/International_Space_Station" title="International Space Station">ISS</a> visiting vehicle safety rules, the primary payload owner is contractually allowed to decline a second reignition. NASA stated that this was because SpaceX could not guarantee a high enough likelihood of the second stage completing the second burn successfully which was required to avoid any risk of secondary payload's collision with the ISS.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-OrbcommTotalLoss_32-0"><a href="#cite_note-OrbcommTotalLoss-32">[26]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sn20121011_33-0"><a href="#cite_note-sn20121011-33">[27]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-34"><a href="#cite_note-34">[28]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">5
</th>
<td>1 March 2013,<br/>15:10
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.0" title="Falcon 9 v1.0">F9 v1.0</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-4"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B0007.1<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-4"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SpaceX_CRS-2" title="SpaceX CRS-2">SpaceX CRS-2</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxManifest20120925_28-1"><a href="#cite_note-sxManifest20120925-28">[22]</a></sup><br/>(Dragon C104)
</td>
<td>4,877 kg (10,752 lb)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a> (<a class="mw-redirect" href="/wiki/ISS" title="ISS">ISS</a>)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/NASA" title="NASA">NASA</a> (<a href="/wiki/Commercial_Resupply_Services" title="Commercial Resupply Services">CRS</a>)
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success
</td>
<td class="table-noAttempt" style="background: #EEE; vertical-align: middle; white-space: nowrap; text-align: center;">No attempt
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">Last launch of the original Falcon 9 v1.0 <a href="/wiki/Launch_vehicle" title="Launch vehicle">launch vehicle</a>, first use of the unpressurized trunk section of Dragon.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxf9_20110321_35-0"><a href="#cite_note-sxf9_20110321-35">[29]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">6
</th>
<td>29 September 2013,<br/>16:00<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-pa20130930_36-0"><a href="#cite_note-pa20130930-36">[30]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.1" title="Falcon 9 v1.1">F9 v1.1</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-MuskMay2012_13-5"><a href="#cite_note-MuskMay2012-13">[7]</a></sup><br/>B1003<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-block_numbers_14-5"><a href="#cite_note-block_numbers-14">[8]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a class="mw-redirect" href="/wiki/Vandenberg_Air_Force_Base" title="Vandenberg Air Force Base">VAFB</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Vandenberg_Space_Launch_Complex_4" title="Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 4">SLC-4E</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/CASSIOPE" title="CASSIOPE">CASSIOPE</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxManifest20120925_28-2"><a href="#cite_note-sxManifest20120925-28">[22]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-CASSIOPE_MDA_37-0"><a href="#cite_note-CASSIOPE_MDA-37">[31]</a></sup>
</td>
<td>500 kg (1,100 lb)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Polar_orbit" title="Polar orbit">Polar orbit</a> <a href="/wiki/Low_Earth_orbit" title="Low Earth orbit">LEO</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Maxar_Technologies" title="Maxar Technologies">MDA</a>
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-pa20130930_36-1"><a href="#cite_note-pa20130930-36">[30]</a></sup>
</td>
<td class="table-no2" style="background: #FFE3E3; color: black; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Uncontrolled<br/><small>(ocean)</small><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-ocean_landing_38-0"><a href="#cite_note-ocean_landing-38">[d]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">First commercial mission with a private customer, first launch from Vandenberg, and demonstration flight of Falcon 9 v1.1 with an improved 13-tonne to LEO capacity.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxf9_20110321_35-1"><a href="#cite_note-sxf9_20110321-35">[29]</a></sup> After separation from the second stage carrying Canadian commercial and scientific satellites, the first stage booster performed a controlled reentry,<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-39"><a href="#cite_note-39">[32]</a></sup> and an <a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_first-stage_landing_tests" title="Falcon 9 first-stage landing tests">ocean touchdown test</a> for the first time. This provided good test data, even though the booster started rolling as it neared the ocean, leading to the shutdown of the central engine as the roll depleted it of fuel, resulting in a hard impact with the ocean.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-pa20130930_36-2"><a href="#cite_note-pa20130930-36">[30]</a></sup> This was the first known attempt of a rocket engine being lit to perform a supersonic retro propulsion, and allowed SpaceX to enter a public-private partnership with <a href="/wiki/NASA" title="NASA">NASA</a> and its Mars entry, descent, and landing technologies research projects.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-40"><a href="#cite_note-40">[33]</a></sup> <small>(<a href="#Maiden_flight_of_v1.1">more details below</a>)</small>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2" scope="row" style="text-align:center;">7
</th>
<td>3 December 2013,<br/>22:41<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sfn_wwls20130624_41-0"><a href="#cite_note-sfn_wwls20130624-41">[34]</a></sup>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Falcon_9_v1.1" title="Falcon 9 v1.1">F9 v1.1</a><br/>B1004
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Force_Station" title="Cape Canaveral Space Force Station">CCAFS</a>,<br/><a href="/wiki/Cape_Canaveral_Space_Launch_Complex_40" title="Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40">SLC-40</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SES-8" title="SES-8">SES-8</a><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sxManifest20120925_28-3"><a href="#cite_note-sxManifest20120925-28">[22]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-spx-pr_42-0"><a href="#cite_note-spx-pr-42">[35]</a></sup><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-aw20110323_43-0"><a href="#cite_note-aw20110323-43">[36]</a></sup>
</td>
<td>3,170 kg (6,990 lb)
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/Geostationary_transfer_orbit" title="Geostationary transfer orbit">GTO</a>
</td>
<td><a href="/wiki/SES_S.A." title="SES S.A.">SES</a>
</td>
<td class="table-success" style="background: #9EFF9E; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Success<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-SNMissionStatus7_44-0"><a href="#cite_note-SNMissionStatus7-44">[37]</a></sup>
</td>
<td class="table-noAttempt" style="background: #EEE; vertical-align: middle; white-space: nowrap; text-align: center;">No attempt<br/><sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-sf10120131203_45-0"><a href="#cite_note-sf10120131203-45">[38]</a></sup>
</td></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="9">First <a href="/wiki/Geostationary_transfer_orbit" title="Geostationary transfer orbit">Geostationary transfer orbit</a> (GTO) launch for Falcon 9,<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-spx-pr_42-1"><a href="#cite_note-spx-pr-42">[35]</a></sup> and first successful reignition of the second stage.<sup class="reference" id="cite_ref-46"><a href="#cite_note-46">[39]</a></sup> SES-8 was inserted into a <a href="/wiki/Geostationary_transfer_orbit" title="Geostationary transfer orbit">Super-Synchronous Transfer Orbit</a> of 79,341 km (49,300 mi) in apogee with an <a href="/wiki/Orbital_inclination" title="Orbital inclination">inclination</a> of 20.55° to the <a href="/wiki/Equator" title="Equator">equator</a>.
</td></tr></tbody></table>